Difference between revisions of "The Great Lakes Water Quality Agreements"
| [unchecked revision] | [unchecked revision] |
(Saved using "Save and continue" button in form) |
|||
| Line 112: | Line 112: | ||
=== Outcome === | === Outcome === | ||
| − | In September 2012, concluding a three-year negotiation process, the United States and Canada signed the newest iteration of the GLWQA (Environment News Service, 2012)<ref name="ENS">U.S., Canada Update Great Lakes Water Quality Protections | Environment News Service. (2012, September 7). Environment News Service RSS. Retrieved May 19, 2014, from http://ens-newswire.com/2012/09/07/u-s-canada-update-great-lakes-water-quality-protections/</ref>. This agreement included many of the same guiding principles from prior agreements, such as a goal for virtual elimination of persistent toxic substance; the LAMPs, which address water quality threats on a lake-wide scale; and AOCs, which focus on the remediation of specific geographic hotspots. However, it also included some key changes, such as an increased emphasis on pollution prevention by setting new phosphorous reduction targets, a focus on prevention of introduction of invasive species, habitat analysis, and mitigation of ships’ ballast water.<ref name="GLWQA 2012">Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement 2012, Canada-United States, September 7, 2012. Retrieved April 28, 2014 from http://www.ijc.org/en_/Great_Lakes_Water_Quality</ref> One of the most celebrated additions was a new focus on the impact of climate change on the Great Lakes.<ref name="EC and USEPA 2014">Environment Canada and USEPA (2014, March 10). binational.net. Retrieved May 6, 2014, from http://www.binational.net/home_e.html</ref> | + | In September 2012, concluding a three-year negotiation process, the United States and Canada signed the newest iteration of the GLWQA (Environment News Service, 2012)<ref name="ENS">U.S., Canada Update Great Lakes Water Quality Protections |
| + | |Summary=The current management structure of the Great Lakes is the product of a fifty-year history of formal agreements between Canada and the United States. The agreements reflect changing understandings of the sources of pollution, evolving beliefs on the role of local stakeholder engagement, and varying levels of political will to commit resources to environmental efforts in Canada and the U.S. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Unfortunately, the Great Lakes have suffered a long history of pollution, encroachment by invasive species, and habitat degradation (USEPA, 2012)<ref name="EPA Concerns">Environmental Protections Agency (2012, June 25). The great lakes today: concerns. USEPA. Retrieved May 6, 2014, from http://www.USEPA.gov/greatlakes/atlas/glat-ch4.html</ref>. The United States and Canada have sought to mitigate these environmental concerns through a series of Water Quality Agreements since 1972. As Botts and Muldoon (2005) argue, these agreements represent “the first success in dealing with a major environmental problem across an international border”<ref name="Botts and Muldoon 2005"/> and reflect both the close relationship between the two countries as well as their abilities to move past key political and cultural differences. While these agreements have arguably made a real impact on the water quality of the Great Lakes, there continues to be a great deal of stress on the lakes from high levels of pollutants. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The extent of stakeholder engagement has been uneven over the years, but has generally increased over time. In the early years, the lack of public involvement in the negotiation of the Great Lakes Water Quality Agreements (GLWQA) was less controversial because mitigation efforts were narrower. At that time, scientists linked pollution primarily to poor sewage treatment systems and phosphates in detergents. In the United States (through the Clean Water Act) and Canada (through the Canada-Ontario Agreement) both federal governments committed substantial resources to mitigation efforts, placing fewer burdens on local actors. Over time, the prevailing knowledge of pollution changed. Scientists now understand that pollutants come from fertilizers, construction activities, storm water runoff, combined sewer overflows, atmospheric depositions, and sediments (LEEP, 2014)<ref name="LEEP Report 2014">Lake Erie Ecosystem Priority (2014). A Balanced Diet for Lake Erie: Reducing Phosphorus Loadings and Harmful Algal Blooms. Report of the International Joint Commission</ref>. Such a complex set of pollutants means that a broader range of stakeholders must be involved in the mitigation activities. While involving more players in implementing the obligations under the GLWQA makes sense, the federal government must provide enough funding to support these efforts. This is especially true if the federal governments do not allow local actors to participate in negotiations on the very agreements that dictate the obligations they expect local actors to fulfill. Recently, however, the track record for doing this is mixed. | ||
| + | |Topic Tags={{Topic Tag | ||
| + | |Topic Tag=invasive species | ||
| + | }}{{Topic Tag | ||
| + | |Topic Tag=climate change | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |External Links= | ||
| + | |Case Review={{Case Review Boxes | ||
| + | |Empty Section=No | ||
| + | |Clean Up Required=No | ||
| + | |Expand Section=No | ||
| + | |Add References=No | ||
| + | |Wikify=No | ||
| + | |connect to www=No | ||
| + | |Out of Date=No | ||
| + | |Disputed=No | ||
| + | |MPOV=No | ||
| + | |ForceDiv=yes | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |Environment News Service. (2012, September 7). Environment News Service RSS. Retrieved May 19, 2014, from http://ens-newswire.com/2012/09/07/u-s-canada-update-great-lakes-water-quality-protections/</ref>. This agreement included many of the same guiding principles from prior agreements, such as a goal for virtual elimination of persistent toxic substance; the LAMPs, which address water quality threats on a lake-wide scale; and AOCs, which focus on the remediation of specific geographic hotspots. However, it also included some key changes, such as an increased emphasis on pollution prevention by setting new phosphorous reduction targets, a focus on prevention of introduction of invasive species, habitat analysis, and mitigation of ships’ ballast water.<ref name="GLWQA 2012">Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement 2012, Canada-United States, September 7, 2012. Retrieved April 28, 2014 from http://www.ijc.org/en_/Great_Lakes_Water_Quality</ref> One of the most celebrated additions was a new focus on the impact of climate change on the Great Lakes.<ref name="EC and USEPA 2014">Environment Canada and USEPA (2014, March 10). binational.net. Retrieved May 6, 2014, from http://www.binational.net/home_e.html</ref> | ||
The plan also expanded the role of public participation. The plan required that progress reports be done every three years, actually a reduction from the previous biennial reporting. Despite this, it allowed for the involvement of more levels of government, non-governmental organizations, and the private sector, by changing the composition of the Water Quality Board to include state, tribal, environmental groups, private business interests, and agricultural groups. This was not only meant to increase stakeholder engagement, but also to allow the Water Quality Board to function as a citizen’s advisory board, with increased independent oversightt.<ref name="communication"/>This greatly increased the public approval of the new agreement. For example, the agreement garnered the support of the 90 mayors that make up an important interest group: The Great Lakes and St. Lawrence Cities Initiative. They felt the agreement provided more latitude for local engagement in the management of the Great Lakes.<ref name="Ullrich, D.">Ullrich, D. (2012, September 7). Mayors Support New Water Quality Agreement. Great Lakes and St. Lawrence Cities Initiative. Retrieved May 8, 2014, from http://www.glslcities.org/news/news.cfm</ref> | The plan also expanded the role of public participation. The plan required that progress reports be done every three years, actually a reduction from the previous biennial reporting. Despite this, it allowed for the involvement of more levels of government, non-governmental organizations, and the private sector, by changing the composition of the Water Quality Board to include state, tribal, environmental groups, private business interests, and agricultural groups. This was not only meant to increase stakeholder engagement, but also to allow the Water Quality Board to function as a citizen’s advisory board, with increased independent oversightt.<ref name="communication"/>This greatly increased the public approval of the new agreement. For example, the agreement garnered the support of the 90 mayors that make up an important interest group: The Great Lakes and St. Lawrence Cities Initiative. They felt the agreement provided more latitude for local engagement in the management of the Great Lakes.<ref name="Ullrich, D.">Ullrich, D. (2012, September 7). Mayors Support New Water Quality Agreement. Great Lakes and St. Lawrence Cities Initiative. Retrieved May 8, 2014, from http://www.glslcities.org/news/news.cfm</ref> | ||
| Line 162: | Line 186: | ||
{{!}} 2012 {{!}}{{!}}New agreement put in place, which takes into account aquatic invasive species, climate change, and groundwater issues. | {{!}} 2012 {{!}}{{!}}New agreement put in place, which takes into account aquatic invasive species, climate change, and groundwater issues. | ||
{{!}}} | {{!}}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 15:54, 21 May 2014
| Geolocation: | 42° 4' 0.7867", -81° 20' 23.789" |
|---|---|
| Total Population | 3535,000,000 millionmillion |
| Total Area | 244,106 km"km" is not declared as a valid unit of measurement for this property. km2 |
| Climate Descriptors | Continental (Köppen D-type) |
| Predominent Land Use Descriptors | agricultural- cropland and pasture, conservation lands, urban- high density |
| Important Uses of Water | Agriculture or Irrigation, Domestic/Urban Supply, Fisheries - farmed, Industry - consumptive use, Recreation or Tourism |
| Water Features: | The Great Lakes |
| Riparians: | United States of America, Canada |
Contents
[hide]Summary
Natural, Historic, Economic, Regional, and Political Framework
Background
Made up of Lake Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie and Ontario, the Great Lakes are the largest freshwater system on Earth. They span more than 750 miles along the border between Canada and the United States and serve as an important resource for consumption, transportation, power, and recreation.[6] About 24 million people in the United States (8% of the U.S. population) and 9.8 million people in Canada (32% of Canada’s population) rely on the Great Lakes for water and jobs.[7]
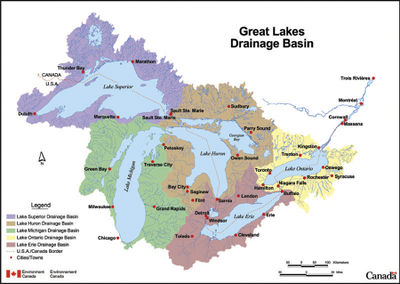
The Great Lakes and their associated basins share a complex border that incorporates multiple jurisdictions and players. At the national level, the Great Lakes cross the Canadian and the United States border. Their watershed incorporates eight U.S. states and two Canadian provinces. At the municipal level, many cities draw on the lakes including Chicago, Toronto, Cleveland, Toledo, Detroit, and Buffalo. The Great Lakes are also home to various tribal groups and first nations within both countries. All of these parties contribute to the contamination of the Great Lakes and therefore must play a role in mitigation efforts.
Additionally, many non-governmental groups have a stake in the management of water quality in the Great Lakes. Many pollutants come from industrial and agricultural activities, a fact which has resulted in efforts to regulate these industries. Additionally, environmental groups are active in pushing for higher water quality standards.
Governance Structure
The management of water quality in the Great Lake is significantly more complicated than the management of water levels within the Great Lakes, because there is no single body in charge of implementing or enforcing water quality objectives. Federal officials from the United States and Canada agree to the terms of the bilateral agreements. Loosely, a binational body called the International Joint Commission (IJC), consisting of six commissioners (three from the United States and three from Canada) monitors and evaluates the water quality within the Great Lakes. The International Joint Commission then makes recommendations to each nation. Other federal, state, and local actors conduct the actual day-to-day pollution mitigation work.
These GLWQA agreements ultimately are not planning documents, which mean that other actors must devise the actual strategies and mechanisms to reach the agreed-upon objectives. This is less controversial when the actor in charge of implementation is the federal government (or when funding from the federal government is plentiful). However, when obligations fall to more local actors, fulfilling these federal obligations is more contentious.
The Boundary Water Treaty of 1909 and the International Joint Commission
The binational management structure of the Great Lakes (and all other water bodies along the Canadian and the United States border) dates back to the Boundary Water Treaty of 1909. This treaty commits both nations to mitigating pollution due to one line within the treaty that reads: “boundary waters and waters flowing across the boundary shall not be polluted on either side to the injury of health or property on the other” (Article IV Boundary Water Treaty of 1909)[8]. While this lays the groundwork for the water quality agreements, it does not specify who will be in charge of actually managing mitigation efforts.
This treaty also established the International Joint Commission (IJC). While the treaty and subsequent agreements clearly designated that the IJC has the authority to manage water levels within the Great Lakes, it is much less clear on the IJC’s role in managing water quality.[9] What the Boundary Waters Treaty does allow the IJC to do is research water quality issues. Article XI of the Boundary Water Treaty specifically grants the IJC power to investigate issues and make recommendations to both nations’ governments. When asked to make a recommendation on a specific issue the IJC “appoints a board with equal numbers of experts from each country” who are “chosen for their professional abilities” rather than as representatives of stakeholders.[10] Historically, both Canada and the United States have been receptive to these experts’ suggestions and attest that this expert driven joint fact-finding method has been key to avoiding disputes.[11]
One former commissioner explained that, without formal decision-making authority, the IJC’s main function with regard to water quality is to act as a bully pulpit to encourage federal action when needed (specifically, they make recommendation on when the existing GLWQA needs updating). They also monitor and support implementation action at the state and local level [12].
The first GLWQA in 1972 created the Great Lakes Regional Office and the Water Quality Board within the IJC to act as the monitoring and evaluation body representing both nations. The exact role of these bodies has changed over time. Currently the Water Quality Board is in charge of making formal recommendations to the IJC. Importantly, the Water Quality Board has become increasingly representative, and now includes representatives of the states, municipalities, the private and non-profit sectors, and tribal groups. The Great Lakes Regional Office is largely a research institution, an oversight body, and a convener of stakeholders.
Canadian Actors
Environment Canada is the prime federal agency that represents Canada in bilateral negotiations and is nominally in charge of implementing the GLWQA. In 1972, the federal government signed the Canada-Ontario Agreement, which stipulates that Ontario is in charge of carrying out the mitigation obligations but will be supported with funding from the federal government. Quebec also plays a role in implementation, but the relationship is not defined by a formal agreement between the federal government and the province.[11]
U.S. Actors
Deriving from the Clean Water Act first passed in 1972, the lead actor in charge of implementing and negotiating the GLWQA in the United States is the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Currently, the Federal Government signs the agreements and provides some funding for implementation, but ultimate authority to set and enforce water quality standards is delegated to the states. Much of the implementation processes filters down another layer to the cities that have historically been blamed for a large share of pollutants (though this blame is shifting to weigh more heavily on the agriculture industry). Historically, both states and municipal governments have complained that the GLWQA creates unfunded mandates. [11]
The Problem:
Pollution issues within the Great Lakes have long been a problem. Public awareness of pollution began in both Canada and the United States following World War II. In 1956 the United States proposed, and Canada agreed to, a request for the IJC to investigate pollution of Lake Erie, Lake Ontario, and the St. Lawrence River. This was later expanded to an even broader study of both water quality and quantity within the lakes due to concerns that water quantity had hit historic lows in the 1960s. Regarding water quality, researchers found that excessive levels of phosphorus contaminated Lake Erie and Lake Ontario, which increased algae growth and depleted oxygen levels. Reacting to these reports, and to an increasingly vocal and concerned public that had embraced the environmental movement of the 1970s, the IJC issued a final report in 1970 recommending a cleanup effort.
Past Agreements
1972 GLWQA
The IJC’s report was used to inform bilateral negotiations between the United States and Canada, resulting in the 1972 GLWQA signed by U.S. President Nixon and Canadian Prime Minister Trudeau. One of the primary areas of disagreement was on the allocation of the right to pollute. Canada argued that it should be allowed to pollute up to 50% of the amount the lakes could withstand, which would mean that the United States had to take on a greater burden of implementing new pollution control measures. Canada, which already had a federal ban on phosphates, proposed a more aggressive phosphate reduction proposal than the United States was ultimately willing to accept. In the end the two countries agreed on a slightly weaker schedule for reduction of phosphorous loading.[13]
This agreement also expanded the role of the IJC to include “collation, analysis, dissemination of data relative to water quality objectives and programs, for giving advice and recommendation to government, and for coordinating joint activities including research.”[13] To fulfill these new functions the IJC established The Great Lakes Water Quality Board, which was made up of federal and state/provincial representatives. While this board advises on, monitors, and assesses the water quality within the Great Lakes, the actual responsibility for pollution control remained the obligation of private citizens, municipal governments, state and provincial leadership, and/or federal offices in each country.[13]
Overall, the success of this agreement was mixed. It created a common dialogue about binational control of pollution while allowing each nation to manage the solutions within its own political system. It also compelled both federal governments to commit funding to mitigation efforts. This did result in some reduction of phosphates within the Great Lakes. It also propelled gains in scientific understanding of pollutants and their effects. Use of the IJC to monitor the lakes created more accountability between governments. However, the lack of enforcement capabilities left the IJC with little power to force action on their recommendations.[11]
1978 GLWQA
The 1972 agreement required that after five years the parties would “review the operation and effectiveness” of the original agreement. This gave the governments an opportunity to act on findings from the inflow of funding and research on The Great Lakes resulting from the 1972 agreement. Of particular salience, scientists found that the presence of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in fish in the Great Lakes was a threat to human health and put the fishing industry in jeopardy. Even more, scientist came to recognize the fallacy that pollutants were exclusively the result of “direct discharge of industrial wastes into waterways or into the air.”[11] This realization meant that simply preventing spills alone would not be enough to clean up the Great Lakes.
Unlike 1972, this agreement was largely negotiated behind closed doors. Neither the public nor the IJC were party to the agreements. Instead, the State Department, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Environment Canada, and the Department of External Affairs led the negotiations. Within these meetings, representatives from the United States pushed Canada to adopt an industrial pollution control program rather than tailor discharge to the assimilative capacity of the receiving water. The United States also wanted Canada to adopt basin-wide water quality standards. Canada rejected both, stating that it should be allowed to meet common objectives through its own methods.[11]
The United States also wanted to eliminate the IJC’s Great Lakes Regional Office in Windsor, which Canada did not allow. Instead, the two sides agreed to limit the regional office’s role to technical assistance and require that the appointed portion of the IJC be in charge of public information. In 1979, the IJC established a standing committee to assist in providing public information, which “stressed that information ought to be provided while studies and activities are being carried out, not just after decisions are made”.[11] The following years saw a rise in civic activity and environmental organizations within the Great Lakes region.
The final agreement took an ecosystem approach to management that would be more integrative than the previous point-source pollution focused approach. It also agreed to “virtual elimination” of toxic substance discharges. While both of these concepts persist, their meanings were not well defined in this agreement and have been contested over the years.[11]
1987 GLWQA
The next full renegotiation of the Water Quality Agreement did not occur until 1987. This round of negotiations was the most inclusive process to date. The negotiation included U.S. representatives from Michigan, Wisconsin, and New York, as well as Canadian representatives from Ontario and Quebec. The parties reviewed reports not only from the IJC, but also from the Royal Society of Canada, the U.S. National Research Council and the U.S. National Academy of Sciences. The recommendations urged the two countries to continue efforts to meet the goals of the 1978 agreement, but also included amendments to increase local involvement.
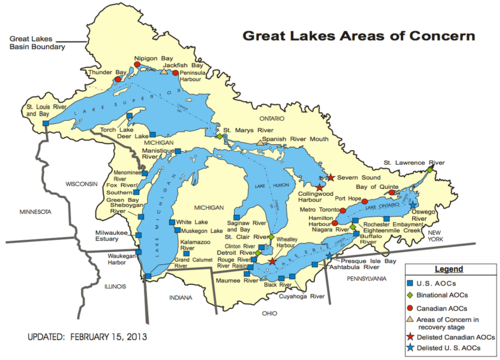
Overall, the changes in the 1987 agreement expanded the participation of local governments, lobbying groups, and citizens, but also set up structures to shift implementation burdens to local actors. Under this agreement the United States and Canada created a framework for Lake-wide Management Plans (LAMPs) and identified hotspots that are called Areas of Concern (AOCs) (see figure 2 for locations of AOCs). Within each LAMP and AOC, local agencies would be required to create what are called Remedial Action Plans (RAPs) that outline their plans for meeting the pollution mitigation obligations in the agreement. While the IJC serves as oversight in each LAMP and AOC, other federal, state/provincial, and local levels of government, as well as the members of the public are in charge of actual planning and remediation implementation.[11]
Additionally, the 1987 agreement requires the IJC to hold biennial meetings in which the Water Quality Board reports on its activities. These serve as opportunities for stakeholders to learn about and participate in water quality management. At this time, local actors started asking for more representation on the Water Quality Board. In addition to wanting a chance to influence policy, some people were concerned that the Water Quality Board could not functionally provide “independent” oversight. They argued that public officials who were in charge of implementation should not be the same people evaluating progress. Despite this criticism, members of the Water Quality Board argued that this structure allowed them to “make things happen” since they could budget and push for the programs they recommended. It also allowed them to use the Water Quality Board meetings as a forum for joint-fact finding and consensus building around agendas.[11]
The Most Recent Agreement
The first three water quality agreements were followed by real improvements in the health of the Great Lakes. Both the United States and Canada made significant investments in sewage treatment plants and in reductions of phosphorous in household detergents. By the end of the 1980s, phosphorous loadings in Lake Erie, the shallowest lake and therefore the most sensitive to pollution, were reduced by more than half from the 1970s levels. Many of the problems of the past appeared to have been reduced or eliminated.
Reflecting subsiding concerns over the health of the Great Lakes, and increasing conservative attitudes in the federal governments of both Canada and the U.S., the following decades saw deep cuts in funding from the federal governments. However, even though major progress had been made, many of these accomplishments were only on the surface. Of the 43 original AOCs, only 4 had been removed from this list of problem areas by 2005.
Embedded in the prior agreement are periodic reviews conducted every two years by the IJC. The IJC and other environmental groups were aware that progress was slower than originally hoped, but did not recommend a renegotiation of the agreement in their 1992 review. Instead they suggested that both countries should “renew and fulfill their commitments and focus on implementation” of the existing agreement. In 1998, reacting to requests for amendments from Transport Canada, and both nation’s coasts guards, the IJC did a more formal review considering possible needs for amendments. They found that many of the annexes of the 1987 GLWQA did not reflect current scientific knowledge of problems in the Great Lakes, and that the language in the agreements was confusing to stakeholders responsible for implementation. Despite these recommendations, USEPA and Environment Canada announced in 2000 that they were not interested in renegotiating the GLWQA.[11]
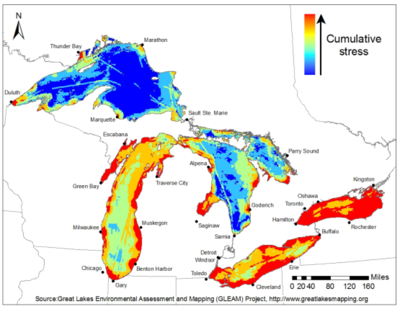
By the early 2000s contamination issues were becoming more severe (LEEP, 2014)[5]. Visible signs of algal blooms, beach closings, and dying fish brought the issue back to the public’s attention.[11] Scientists acknowledged that all of the Great Lakes were showing signs of stress, including “toxic contaminants, invasive species, nutrient loading, shoreline and upland land use changes and hydrologic modifications.”[14] In addition, in May 2000, over 2,000 people in the small town of Walkerton, Ontario became ill from their water supply being contaminated with E. coli. This prompted an inquiry that found that federal funding cuts to the Ministry of Environment in Canada had resulted in a 43% reduction in staff. People linked the inadequacy of funding to the gaps in oversight that allowed the E. coli to surface. Around this same time the U.S. Government Accountability Office found that the U.S. federal government was neglecting their commitments to mitigation. A study on the remedial action plans within the AOCs, found that declines in federal funding paired with little leadership from USEPA had resulted in general neglect. While the federal governments assumed that states would shoulder the burden, the states did not feel it was their responsibility to pay for the programs agreed to by the federal government if the federal governments did not do their part.[11]
Reacting to the increasing negative reviews of the progress being made under the current agreement, the IJC’s 2004 biennial review triggered a more in-depth analysis of the lakes in 2006 and 2007. For this, they engaged over 350 self-selected stakeholders from both Canada and the United States. These groups were organized into nine Review Working Groups (RWGs). Their recommendations were passed on to an Agreement Review Committee (ARC), which compiled ideas into a final report.[14][15] The final report found that the existing GLWQA was “outdated” and suggested that the “Agreement should be revised to specifically address today’s pressing issues, including the impacts of climate change, aquatic invasive species and urbanization."[15]
This report also recommended that a new agreement should include clear implementation mechanisms and recognized the need for “effective coordination and collaboration with other orders of government engaged in implementation” such as states, provinces, cities, first nations and tribal governments. Overall, the report called for increased accountability, which could be accomplished through better coordination with key partners and funding mechanisms to support mandates.[15]
Attempts at Conflict Management
Based on these recommendations, Secretary of State Hillary Clinton and Foreign Minister Lawrence Cannon announced a new round of negotiations for the GLWQA on June 13, 2009. The first formal meetings were held in January 2010 between senior officials from Environment Canada, Foreign Affairs and International Trade Canada, the U.S. Department of State and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. While the meetings were closed to the public, a summary document reported that both countries agreed to a negotiation timeline that aimed to be completed by the end of 2010, but would later be extended. The summary also explained that both governments would engage the public during the process.[14]
Over the next few months, both countries organized a number of webinar series and processes to collect written comments from the public. Each country also agreed to host one public forum. In his analysis, Krantzberg argues that the webinars were viewed as duplicative of the earlier review process, rehashing old issues rather than seeking comment on specific new proposals.[14] Even when topics included clear advancements, the matters presented for discussions tended to leave little room for substantive conversation. Prior to the public forums, participants equally complained that “almost no information has been available to the public about the substance and scope of the new agreement, making it difficult for concerned citizens to ascertain what modernization looks like, or to provide meaningful feedback in public forums."[16] One IJC staff member explained that the Canadian delegation organized a formal citizen’s advisory group that was allowed to view a draft agreement, but could not retain copies. While non-governmental groups called for something similar in the U.S., this did not occur[3].
The IJC was not a direct participant in these negotiations, though it was provided draft language twice and asked to comment. [3]
Outcome
In September 2012, concluding a three-year negotiation process, the United States and Canada signed the newest iteration of the GLWQA (Environment News Service, 2012)Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag. The United States and Canada have sought to mitigate these environmental concerns through a series of Water Quality Agreements since 1972. As Botts and Muldoon (2005) argue, these agreements represent “the first success in dealing with a major environmental problem across an international border”[11] and reflect both the close relationship between the two countries as well as their abilities to move past key political and cultural differences. While these agreements have arguably made a real impact on the water quality of the Great Lakes, there continues to be a great deal of stress on the lakes from high levels of pollutants.
The extent of stakeholder engagement has been uneven over the years, but has generally increased over time. In the early years, the lack of public involvement in the negotiation of the Great Lakes Water Quality Agreements (GLWQA) was less controversial because mitigation efforts were narrower. At that time, scientists linked pollution primarily to poor sewage treatment systems and phosphates in detergents. In the United States (through the Clean Water Act) and Canada (through the Canada-Ontario Agreement) both federal governments committed substantial resources to mitigation efforts, placing fewer burdens on local actors. Over time, the prevailing knowledge of pollution changed. Scientists now understand that pollutants come from fertilizers, construction activities, storm water runoff, combined sewer overflows, atmospheric depositions, and sediments (LEEP, 2014)[5]. Such a complex set of pollutants means that a broader range of stakeholders must be involved in the mitigation activities. While involving more players in implementing the obligations under the GLWQA makes sense, the federal government must provide enough funding to support these efforts. This is especially true if the federal governments do not allow local actors to participate in negotiations on the very agreements that dictate the obligations they expect local actors to fulfill. Recently, however, the track record for doing this is mixed.
Analysis, Synthesis, and Insight
Individuals may add their own Analysis, Synthesis, and Insight (ASI) to a case. ASI sub-articles are protected, so that each contributor retains authorship and control of their own content. Edit the case to add your own ASI.
Learn moreASI:Analysis of the Water Diplomacy Framework
(last edit: 18 May 2014)
Tagged with: invasive species climate change
- ^ Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement 2012, Canada-United States, September 7, 2012. Retrieved April 28, 2014 from http://www.ijc.org/en_/Great_Lakes_Water_Quality
- ^ Environment Canada and USEPA (2014, March 10). binational.net. Retrieved May 6, 2014, from http://www.binational.net/home_e.html
- ^ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 IJC U.S. Staff member, personal communication with AquaPedia user Mdeas, 2014
- ^ Ullrich, D. (2012, September 7). Mayors Support New Water Quality Agreement. Great Lakes and St. Lawrence Cities Initiative. Retrieved May 8, 2014, from http://www.glslcities.org/news/news.cfm
- ^ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Lake Erie Ecosystem Priority (2014). A Balanced Diet for Lake Erie: Reducing Phosphorus Loadings and Harmful Algal Blooms. Report of the International Joint Commission
- ^ Environmental Protection Agency. (2012, June 5). Great Lakes Basic Information. USEPA. Retrieved May 6, 2014, from http://www.epa.gov/greatlakes/basicinfo.html
- ^ University of Wisconsin, Sea Grant. (n.d.). Great Lakes and Wisconsin Water Facts. Retrieved May 8, 2014, from http://www.seagrant.wisc.edu/Home/AboutUsSection/PressRoom/Details.aspx?PostID=796
- ^ Boundary Waters Treaty of 1909, Great Britain-United States, May 5, 1910. Retrieved April 28, 2014 from http://ijc.org/en_/BWT
- ^ Yaskowitz, D.(2005) US/Canadian Boundaries Water Treaty and The GLWQA. Water Encyclopedia.
- ^ International Joint Commission (2014). A Balanced Diet for Lake Erie: Reducing Phosphorus Loadings and Harmful Algal Blooms. Report of the Lake Erie Ecosystem Priority.
- ^ 11.00 11.01 11.02 11.03 11.04 11.05 11.06 11.07 11.08 11.09 11.10 11.11 11.12 11.13 Botts, L., & Muldoon, P. R. (2005). Evolution of the GLWQA. East Lansing: Michigan State University Press.
- ^ IJC; Former U.S. Commissioner,, personal communication with AquaPedia user Mdeas, 2014
- ^ 13.0 13.1 13.2 Carroll, J. E. (1983). Environmental diplomacy: an examination and a prospective of Canadian-U.S. transboundary environmental relations. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press.
- ^ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 Krantzberg, G. (2012) Renegotiation of the 1987 GLWQA: From Confusion to Promise. Sustainability, 1239-1255.
- ^ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Agreement Review Committee (2007). Review of the GLWQA prepared for The Great Lakes Binational Executive Committee.
- ^ Jackson, J. (2011, September 12). Press Release: Great Lakes Leaders Urge Diplomats to Include Essentials in New Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement. RSS. Retrieved May 8, 2014, from http://lakemichiganforum.org/news/stories/read/2011-09_press-release-great-lakes-leaders-urg