Difference between revisions of "Transboundary Dispute Resolution: U.S./Mexico Shared Aquifers"
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
Mpritchard (Talk | contribs) |
Mpritchard (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
The border region between the United States and Mexico has fostered its share of surface-water conflict, from the Colorado River to the Rio Grande/Rio Bravo River. It has also been a model for peaceful conflict resolution, notably the work of the International Boundary and Water Commission (IBWC), the supra-legal body established to manage shared water resources as a consequence of the 1944 US-Mexico Water Treaty. Yet the difficulties encountered in managing shared surface-water pale in comparison to trying to allocate groundwater resources-each aquifer system is generally not understood as gathering information on aquifers is very costly and the science of groundwater is still inexact. This makes negotiations over a shared aquifer system very difficult. | The border region between the United States and Mexico has fostered its share of surface-water conflict, from the Colorado River to the Rio Grande/Rio Bravo River. It has also been a model for peaceful conflict resolution, notably the work of the International Boundary and Water Commission (IBWC), the supra-legal body established to manage shared water resources as a consequence of the 1944 US-Mexico Water Treaty. Yet the difficulties encountered in managing shared surface-water pale in comparison to trying to allocate groundwater resources-each aquifer system is generally not understood as gathering information on aquifers is very costly and the science of groundwater is still inexact. This makes negotiations over a shared aquifer system very difficult. | ||
| − | + | In a 1988 Center for U.S. - Mexican Studies Report, Mumme identified 23 sites in contention in six different hydrogeologic regions along the 3,300 kilometers of shared boundary.<ref name ="Mumme 1988">Mumme, S. 1988. "Apportioning Groundwater Beneath the U.S.- Mexico Border: Obstacles and Alternatives." Center for U.S.- Mexican Studies Report Series 45.</ref> While the 1944 Treaty mentions the importance of resolving the allocations of groundwater between the two states, it does not do so. In fact, shared surface-water resources were the focus of the IBWC until the early 1960s, when a U.S. irrigation district began draining saline groundwater into the Colorado River and deducting the quantity of saline water from Mexico 's share of freshwater. In response, Mexico began a "crash program" of groundwater development in the border region, to make up the losses. | |
|Issues= | |Issues= | ||
|ASI= | |ASI= | ||
Revision as of 11:51, 21 August 2012
| Geolocation: | 31° 46' 12.7463", -106° 29' 45.497" |
|---|---|
| Total Population | 22,874,80022,874,800,000,000 millionmillion |
| Total Area | 1,310,6301,310,630 km² 506,034.243 mi² km2 |
| Climate Descriptors | Semi-arid/steppe (Köppen B-type), Arid/desert (Köppen B-type), Humid mid-latitude (Köppen C-type), Dry-summer, Dry-winter |
| Predominent Land Use Descriptors | agricultural- cropland and pasture, rangeland, urban |
| Important Uses of Water | Agriculture or Irrigation, Domestic/Urban Supply, Recreation or Tourism |
Contents
Summary
The border region between the United States and Mexico has fostered its share of surface-water conflict, from the Colorado River to the Rio Grande/Rio Bravo River. It has also been a model for peaceful conflict resolution, notably the work of the International Boundary and Water Commission (IBWC), the supra-legal body established to manage shared water resources as a consequence of the 1944 US-Mexico Water Treaty. Yet the difficulties encountered in managing shared surface-water pale in comparison to trying to allocate groundwater resources-each aquifer system is generally not understood as gathering information on aquifers is very costly and the science of groundwater is still inexact. This makes negotiations over a shared aquifer system very difficult. The complications of groundwater are exemplified in the border region between the United States and Mexico where, despite the presence of an active supra-legal authority since 1944, groundwater issues have yet to be resolved. Mentioned as vital in the 1944 Treaty, and again in 1973, the difficulties in quantifying the ambiguities inherent in groundwater regimes has eluded legal and management experts ever since. Even after three decades of having problems with the 1944 Treaty and groundwater issues, there does not appear to be a movement towards a new agreement referring to the United States-Mexican shared aquifers anytime soon, although Mumme[1] states that it is likely that "some form of systematic cooperation will emerge" between stakeholders in more local areas along the border.
Natural, Historic, Economic, Regional, and Political Framework
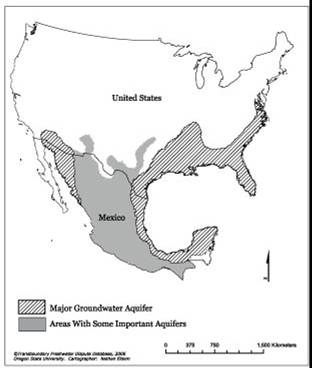 Image 1. Map of shared (transboundary) aquifers between Mexico and U.S[2]
Image 1. Map of shared (transboundary) aquifers between Mexico and U.S[2]
Background
The border region between the United States and Mexico has fostered its share of surface-water conflict, from the Colorado River to the Rio Grande/Rio Bravo River. It has also been a model for peaceful conflict resolution, notably the work of the International Boundary and Water Commission (IBWC), the supra-legal body established to manage shared water resources as a consequence of the 1944 US-Mexico Water Treaty. Yet the difficulties encountered in managing shared surface-water pale in comparison to trying to allocate groundwater resources-each aquifer system is generally not understood as gathering information on aquifers is very costly and the science of groundwater is still inexact. This makes negotiations over a shared aquifer system very difficult.
In a 1988 Center for U.S. - Mexican Studies Report, Mumme identified 23 sites in contention in six different hydrogeologic regions along the 3,300 kilometers of shared boundary.[3] While the 1944 Treaty mentions the importance of resolving the allocations of groundwater between the two states, it does not do so. In fact, shared surface-water resources were the focus of the IBWC until the early 1960s, when a U.S. irrigation district began draining saline groundwater into the Colorado River and deducting the quantity of saline water from Mexico 's share of freshwater. In response, Mexico began a "crash program" of groundwater development in the border region, to make up the losses.
Analysis, Synthesis, and Insight
Individuals may add their own Analysis, Synthesis, and Insight (ASI) to a case. ASI sub-articles are protected, so that each contributor retains authorship and control of their own content. Edit the case to add your own ASI.
Learn moreContributed by: Aaron T. Wolf, Joshua T. Newton, Matthew Pritchard (last edit: 12 February 2013)
- ^ Mumme, S. (2004). Advancing binational cooperation in the transboundary aquifer management on the U.S.-Mexico Border. Paper presented at Groundwater in the West Conference, University of Colorado at Boulder.
- ^ Product of the Transboundary Freshwater Dispute Database, Department of Geosciences, Oregon State University. Additional information about the TFDD can be found at: http://www.transboundarywaters.orst.edu/research/case_studies/US_Mexico_Aquifer_New.htm
- ^ Mumme, S. 1988. "Apportioning Groundwater Beneath the U.S.- Mexico Border: Obstacles and Alternatives." Center for U.S.- Mexican Studies Report Series 45.



